Understanding ContentProvider in Android
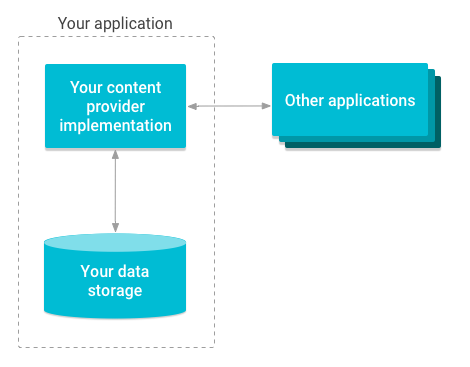
When it comes to sharing data between different apps in Android, ContentProvider is a powerful component that enables developers to do so. A ContentProvider acts as an interface between an app’s data and other apps. In this article, we will explore what ContentProvider is, how it works, and how to create a simple ContentProvider in Android.
What is ContentProvider?
In Android, ContentProvider is a component that provides a standardized interface to access and manipulate data stored in an app’s database or file system. This data can be accessed by any app that has permission to do so. ContentProvider is responsible for managing access to data, enforcing permissions, and providing a way to query data.
How ContentProvider works?
A ContentProvider is implemented as a subclass of the android.content.ContentProvider class. It provides a set of methods that other apps can use to query, insert, update, or delete data. These methods are:
query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder): This method is used to retrieve data from the ContentProvider. It takes aUriobject that specifies the data to retrieve, an array ofStringobjects that specifies which columns to include, aStringobject that specifies the selection criteria, an array ofStringobjects that specifies the selection arguments, and aStringobject that specifies the sort order.insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values): This method is used to insert new data into the ContentProvider. It takes aUriobject that specifies where to insert the data and aContentValuesobject that contains the data to insert.update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs): This method is used to update existing data in the ContentProvider. It takes aUriobject that specifies which data to update, aContentValuesobject that contains the new data to update, aStringobject that specifies the selection criteria, and an array ofStringobjects that specifies the selection arguments.delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs): This method is used to delete data from the ContentProvider. It takes aUriobject that specifies which data to delete, aStringobject that specifies the selection criteria, and an array ofStringobjects that specifies the selection arguments.
To access a ContentProvider, an app needs to know the Uri of the data it wants to access and the permissions required to access that data. Once the app has the Uri, it can use the ContentResolver class to interact with the ContentProvider. The ContentResolver class provides methods to query, insert, update, and delete data from the ContentProvider.
Creating a simple ContentProvider
To create a simple ContentProvider, we need to implement the query, insert, update, and delete methods of the android.content.ContentProvider class. For this example, we will create a ContentProvider that manages a list of books.
First, we need to define a Uri that identifies the data we want to share. We will use the following Uri:
public static final Uri CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse("content://com.example.provider/book");
This Uri identifies the data as books and is used to access the ContentProvider.
Next, we need to define the database schema. For this example, we will use a simple database schema that consists of a table named book with three columns: _id, title, and author. We will create a SQLiteOpenHelper class to manage the database.
public class BookDatabaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static final String DATABASE_NAME = "book.db";
private static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
public BookDatabaseHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
db.execSQL("CREATE TABLE book (_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, "
+ "title TEXT NOT NULL, author TEXT NOT NULL);");
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
db.execSQL("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS book");
onCreate(db);
}
}
Now, we can implement the query, insert, update, and delete methods of the ContentProvider class.
public class BookProvider extends ContentProvider {
private BookDatabaseHelper dbHelper;
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
dbHelper = new BookDatabaseHelper(getContext());
return true;
}
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query("book", projection, selection, selectionArgs, null, null, sortOrder);
return cursor;
}
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
long id = db.insert("book", null, values);
return Uri.withAppendedPath(CONTENT_URI, Long.toString(id));
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
int count = db.update("book", values, selection, selectionArgs);
return count;
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
int count = db.delete("book", selection, selectionArgs);
return count;
}
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
return null;
}
}
In this implementation, we first initialize the BookDatabaseHelper in the onCreate method. The query, insert, update, and delete methods use the SQLiteDatabase class to access the database and manipulate data. Finally, the getType method returns null because we do not support any specific MIME types for the data.
Example 1 - How to Load Contacts from the device.
This example examines how to use content provider to load contacts from any android device.
Step 1: Dependencies
No third party dependency is needed.
Step 2: Add Permissions
To read contacts from a user's device, you need permission from the user. Thus you need to add the READ_CONTACTS permission which will be shown to the user when the user is installing your app.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS"/>
Step 3: Design UI
The UI will comprise a button a listview. The user presses the button and contacts are fetched and loaded onto the listview.
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.parag.contentprovidersample.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Get contact names"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
/>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_below="@+id/btn"
android:layout_margin="10dp"/>
</RelativeLayout>
Step 3: Write Code
The code is in java but can be converted to kotlin.
MainActivity.java
Add imports including the LoaderManager and cursorLoader:
import android.app.LoaderManager;
import android.content.CursorLoader;
import android.content.Loader;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.provider.ContactsContract;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ListView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
Extend the appcompactivity and implement several interfaces including the LoaderManager.LoaderCallbacks<Cursor>:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener,LoaderManager.LoaderCallbacks<Cursor>{
Declare our UI widgets as well as projection:
Button button;
ListView listView;
String[] projection = {ContactsContract.Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME};
boolean hasLoaded;
Here's the rest of the code:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn);
listView = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.listview);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public Loader<Cursor> onCreateLoader(int i, Bundle bundle) { // CursorLoader instance
Uri uri = ContactsContract.Contacts.CONTENT_URI;
String orderBy = ContactsContract.Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME_PRIMARY;
if(i == 1) {
return new CursorLoader(this,uri ,projection,null,null,orderBy);
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
@Override
public void onLoadFinished(Loader<Cursor> loader, Cursor cursor) {
ArrayList<String> contactList = new ArrayList<>();
if(cursor != null && cursor.getCount() > 0)
{
while(cursor.moveToNext())
{
contactList.add(cursor.getString(0));
}
ArrayAdapter<String> contactArrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this,android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,contactList);
listView.setAdapter(contactArrayAdapter);
}
}
@Override
public void onLoaderReset(Loader<Cursor> loader) {
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId())
{
case R.id.btn:
if(!hasLoaded)
{
getLoaderManager().initLoader(1,null,this);
hasLoaded = true;
}
else
{
getLoaderManager().restartLoader(1,null,this);
}
}
}
}
Reference
| No. | Name |
|---|---|
| 1. | Download Now |
| 2. | Visit Author |
Example 2: ## Kotlin Android ContentProviders, Room MVVM Example
In this tutorial you will learn how to implement your own ContentProvider to access data from a Room Database via the MVVM design pattern.
Step 1: Create Project
Start by creating an empty Android Studio project.
Step 2: Dependencies
In your app/build.gradle addd the following dependencies:
//Anko to async load data from room
implementation "org.jetbrains.anko:anko-common:$ankoVersion"
implementation "android.arch.persistence.room:runtime:$roomVersion"
kapt "android.arch.persistence.room:compiler:$roomVersion"
annotationProcessor "android.arch.persistence.room:compiler:$roomVersion"
Step : Create Model class
Villains.kt
import androidx.room.ColumnInfo
import androidx.room.Entity
import androidx.room.PrimaryKey
import android.content.ContentValues
import android.provider.BaseColumns
@Entity(tableName = Villains.TABLE_NAME)
data class Villains(
@ColumnInfo(name = VILLAIN_NAME)
var villainName: String,
@ColumnInfo(name = VILLAIN_SERIES)
var villainSeries: String,
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
@ColumnInfo(index = true, name = COLUMN_ID)
var id: Long = 0) {
companion object {
const val COLUMN_ID = BaseColumns._ID
const val TABLE_NAME = "villains"
const val VILLAIN_NAME = "villain_name"
const val VILLAIN_SERIES = "series"
val villainsName = listOf("Joker", "DeathStroke", "Reverse Flash", "Lex Luthor", "Harley Quinn")
val villainsSeries = listOf("Batman", "Arrow", "Flash", "Superman", "Suicide Squad")
var villain: Villains = Villains("", "")
fun fromContentValues(vals: ContentValues): Villains {
if (vals.containsKey(COLUMN_ID)) {
villain.id = vals.getAsLong(COLUMN_ID)
}
if (vals.containsKey(VILLAIN_NAME)) {
villain.villainName = vals.getAsString(VILLAIN_NAME)
}
if (vals.containsKey(VILLAIN_SERIES)) {
villain.villainSeries = vals.getAsString(VILLAIN_SERIES)
}
return villain
}
}
}
Step : Create Dao Interface
VillainsDao.kt
import androidx.room.Dao
import androidx.room.Insert
import androidx.room.Query
import android.database.Cursor
import androidx.room.Update
@Dao
interface VillainsDao {
@Query("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM " + Villains.TABLE_NAME)
fun count(): Int
@Query("SELECT * FROM " + Villains.TABLE_NAME)
fun selectAll(): Cursor
@Insert
fun insert(villains: Villains): Long
@Query("DELETE FROM " + Villains.TABLE_NAME + " WHERE " + Villains.COLUMN_ID + " = :id")
fun deleteById(id: Long): Int
@Query("SELECT * FROM " + Villains.TABLE_NAME + " WHERE " + Villains.COLUMN_ID + " = :id")
fun selectById(id: Long): Cursor
@Update
fun update(villains: Villains): Int
}
Step : Create Room Database
VillainsDatabase.kt
package com.developers.contentproviders.data
import androidx.room.Database
import androidx.room.Room
import androidx.room.RoomDatabase
import android.content.Context
@Database(entities = arrayOf(Villains::class), version = 1)
abstract class VillainsDatabase : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun villainDao(): VillainsDao
companion object {
private lateinit var villainDatabase: VillainsDatabase
fun villainDatabaseInstance(context: Context): VillainsDatabase {
villainDatabase = Room.databaseBuilder(context,
VillainsDatabase::class.java, "room-db").build()
villainDatabase.insertDummyData()
return villainDatabase
}
}
private fun insertDummyData() {
if (villainDao().count() == 0) {
beginTransaction()
try {
for (i in 0..4) {
val villain = Villains(Villains.villainsName[i], Villains.villainsSeries[i])
villainDao().insert(villain)
}
setTransactionSuccessful()
} catch (exception: Exception) {
exception.printStackTrace()
} finally {
endTransaction()
}
}
}
}
Step : Create a ContentProvider
VillainProvider.kt
import android.content.*
import android.database.Cursor
import android.net.Uri
import com.developers.contentproviders.data.Villains
import com.developers.contentproviders.data.VillainsDatabase
class VillainProvider : ContentProvider() {
companion object {
val AUTHORITY: String = "com.developers.contentproviders"
val uri = Uri.parse("content://" + AUTHORITY + "/" + Villains.TABLE_NAME)
val CODE_VILLAINS_ALL = 1
val CODE_VILLAIN_ITEM = 2
val MATCHER = UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH)
init {
MATCHER.addURI(AUTHORITY, Villains.TABLE_NAME, CODE_VILLAINS_ALL)
MATCHER.addURI(AUTHORITY, Villains.TABLE_NAME + "/*", CODE_VILLAIN_ITEM)
}
}
override fun delete(uri: Uri, selection: String?, selectionArgs: Array<String>?): Int {
// Implement this to handle requests to delete one or more rows.
when(MATCHER.match(uri)){
CODE_VILLAINS_ALL->{
throw IllegalArgumentException("Invalid URI, cannot update without ID" + uri);
}
CODE_VILLAIN_ITEM->{
val count = VillainsDatabase.villainDatabaseInstance(context).villainDao()
.deleteById(ContentUris.parseId(uri))
context.getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null)
return count
}
else->{
throw IllegalArgumentException("\"Unknown URI: \" + uri")
}
}
}
override fun getType(uri: Uri): String? {
// at the given URI for getting MIME TYPE
when (MATCHER.match(uri)) {
CODE_VILLAINS_ALL ->
return ContentResolver.CURSOR_DIR_BASE_TYPE + "/" + AUTHORITY + Villains.TABLE_NAME
CODE_VILLAIN_ITEM ->
return ContentResolver.CURSOR_ITEM_BASE_TYPE + "/" + AUTHORITY + Villains.TABLE_NAME
else ->
throw IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI: " + uri)
}
}
override fun insert(uri: Uri, values: ContentValues?): Uri? {
//for insertion of contentValues
when (MATCHER.match(uri)) {
CODE_VILLAINS_ALL -> {
val id = VillainsDatabase.villainDatabaseInstance(context).villainDao()
.insert(Villains.fromContentValues(values as ContentValues))
context.contentResolver.notifyChange(uri, null)
VillainsDatabase.villainDatabaseInstance(context).close()
return ContentUris.withAppendedId(uri, id)
}
CODE_VILLAIN_ITEM -> {
throw IllegalArgumentException("Invalid URI, cannot insert with ID: " + uri)
}
else -> {
throw IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI: " + uri);
}
}
}
override fun onCreate(): Boolean {
// TODO: Implement this to initialize your content provider on startup.
return true
}
override fun query(uri: Uri, projection: Array<String>?, selection: String?,
selectionArgs: Array<String>?, sortOrder: String?): Cursor? {
val code = MATCHER.match(uri)
if (code == CODE_VILLAINS_ALL || code == CODE_VILLAIN_ITEM) {
val villain = VillainsDatabase.villainDatabaseInstance(context).villainDao()
if (code == CODE_VILLAINS_ALL) {
val cursor = villain.selectAll()
cursor.setNotificationUri(context.getContentResolver(), uri)
return cursor
} else {
val cursor = villain.selectById(ContentUris.parseId(uri))
cursor.setNotificationUri(context.getContentResolver(), uri)
return cursor
}
} else {
throw java.lang.IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI: " + uri)
}
}
override fun update(uri: Uri, values: ContentValues?, selection: String?,
selectionArgs: Array<String>?): Int {
when (MATCHER.match(uri)) {
CODE_VILLAINS_ALL -> {
throw IllegalArgumentException("Invalid URI, cannot update without ID" + uri);
}
CODE_VILLAIN_ITEM -> {
val villains = Villains.fromContentValues(values as ContentValues)
villains.id = ContentUris.parseId(uri)
val count = VillainsDatabase.villainDatabaseInstance(context).villainDao().update(villains)
context.getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null)
return count
}
else -> {
throw java.lang.IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI: " + uri)
}
}
}
}
Step : Create RecyclerView Adapter
VillainAdapter.kt
import android.content.Context
import android.database.Cursor
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import com.developers.contentproviders.MainActivity
import com.developers.contentproviders.R
import com.developers.contentproviders.data.Villains
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.item_row.view.*
import java.util.logging.Logger
class VillainAdapter(val context: Context) : RecyclerView.Adapter<VillainAdapter.MyViewHolder>() {
lateinit var mCursor: Cursor
companion object {
val log = Logger.getLogger(MainActivity::class.java.name)
}
override fun getItemCount(): Int {
if(mCursor.count>0){
return mCursor.count
}
else{
return 0
}
}
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): MyViewHolder {
val view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.item_row, parent, false)
return MyViewHolder(view)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: MyViewHolder, position: Int) {
if (mCursor.moveToPosition(position)) {
holder?.bindItems(mCursor)
}
}
class MyViewHolder(itemView: View) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(itemView) {
fun bindItems(cursor: Cursor) {
itemView.name_text_view.text =cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(Villains.VILLAIN_NAME))
itemView.id_text_view.text = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(Villains.COLUMN_ID)).toString()
itemView.series_text_view.text = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(Villains.VILLAIN_SERIES))
}
}
fun setVillains(cursor: Cursor) {
mCursor = cursor
notifyDataSetChanged()
}
}
Step : Create MainActivity
MainActivity.kt
import android.content.ContentValues
import android.database.Cursor
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.loader.app.LoaderManager
import androidx.loader.content.CursorLoader
import androidx.loader.content.Loader
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager
import com.developers.contentproviders.adapter.VillainAdapter
import com.developers.contentproviders.data.Villains
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
import org.jetbrains.anko.doAsync
import java.util.logging.Logger
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), LoaderManager.LoaderCallbacks<Cursor> {
private lateinit var mAdapter: VillainAdapter
companion object {
const val LOADER_VILLAIN = 1
val log = Logger.getLogger(MainActivity::class.java.name)
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(applicationContext)
doAsync {
//Insert through content provider
val values = ContentValues()
values.put(Villains.VILLAIN_NAME, "Gustavo Fring")
values.put(Villains.VILLAIN_SERIES, "Breaking Bad")
contentResolver.insert(VillainProvider.uri, values)
}
layoutManager.orientation = LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL
recycler_view.layoutManager = layoutManager
supportLoaderManager.initLoader(LOADER_VILLAIN, null, this)
}
override fun onCreateLoader(id: Int, args: Bundle?): Loader<Cursor> {
when (id) {
LOADER_VILLAIN -> {
return CursorLoader(applicationContext, VillainProvider.uri, arrayOf(Villains.VILLAIN_NAME,
Villains.VILLAIN_SERIES, Villains.COLUMN_ID), null, null, null)
}
else -> {
throw IllegalArgumentException()
}
}
}
override fun onLoaderReset(loader: Loader<Cursor>) {
when (loader.id) {
LOADER_VILLAIN -> {
log.info("In RESET")
}
}
}
override fun onLoadFinished(loader: Loader<Cursor>, data: Cursor?) {
when (loader.id) {
LOADER_VILLAIN -> {
mAdapter = VillainAdapter(applicationContext)
recycler_view.adapter = mAdapter
mAdapter.setVillains(data as Cursor)
}
}
}
}
Run
Copy the code or download it in the link below, build and run.
Reference
Here are the reference links:
| Number | Link |
|---|---|
| 1. | Download Example |
| 2. | Follow code author |
| 3. | Code: Apache 2.0 License |
Conclusion
ContentProvider is an essential component in Android that enables developers to share data between different apps. In this article, we explored what ContentProvider is, how it works, and how to create a simple ContentProvider in Android. By mastering ContentProvider, developers can build powerful and flexible apps that can share data with other apps.