Understanding AndroidX Preference Library in Android
AndroidX Preference library is a library that is part of the Android Jetpack, which provides a simple and efficient way to store and retrieve application settings or preferences. Using this library, developers can create a user interface that allows users to easily modify the settings of an application.
Features of AndroidX Preference Library
- Simple and easy to use API
- Provides a consistent look and feel across different Android versions
- Supports different types of preferences such as CheckBoxPreference, EditTextPreference, ListPreference, etc.
- Supports creating custom preferences
- Supports storing preferences in different storage backends such as SharedPreferences, SQLite, etc.
- Supports preference dependencies, allowing developers to create dynamic preferences based on user input
Getting Started
To use AndroidX Preference library in your Android project, you need to add the following dependency to your app-level build.gradle file:
implementation 'androidx.preference:preference:1.1.1'
Creating Preferences
To create a preference, you need to define it in an XML file. For example, to create a CheckBoxPreference, you can define it as follows:
<CheckBoxPreference
android:key="my_checkbox_preference"
android:title="My Checkbox Preference"
android:summary="This is a checkbox preference"
android:defaultValue="false" />
In the above code, the key attribute is used to uniquely identify the preference, the title attribute is used to set the title of the preference, the summary attribute is used to provide a description of the preference, and the defaultValue attribute is used to set the default value of the preference.
Once you have defined the preference in an XML file, you can add it to a PreferenceScreen using the following code:
public class MySettingsActivity extends PreferenceActivity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
addPreferencesFromResource(R.xml.preferences);
}
}
In the above code, the addPreferencesFromResource() method is used to load the preferences from the XML file and add them to the PreferenceScreen.
Retrieving Preferences
To retrieve the value of a preference, you can use the following code:
SharedPreferences preferences = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(this);
boolean myCheckboxPreferenceValue = preferences.getBoolean("my_checkbox_preference", false);
In the above code, the getDefaultSharedPreferences() method is used to get the instance of the SharedPreferences object, and the getBoolean() method is used to retrieve the value of the preference.
More about Preferences
The Preference library allows you to build interactive settings screens, without needing to handle interacting with device storage or managing the user interface.
Settings
Settings allow users to change the functionality and behavior of an application. Settings can affect background behavior, such as how often the application synchronizes data with the cloud, or they can be more wide-reaching, such as changing the contents and presentation of the user interface.
The recommended way to integrate user configurable settings into your application is to use the AndroidX Preference Library. This library manages the user interface and interacts with storage so that you define only the individual settings that the user can configure. The library comes with a Material theme that provides a consistent user experience across devices and OS versions.
How to create a Settings Screen
You can create a Settings screen in two way: via xml or via code. Here is the screen that we will build in the two ways:
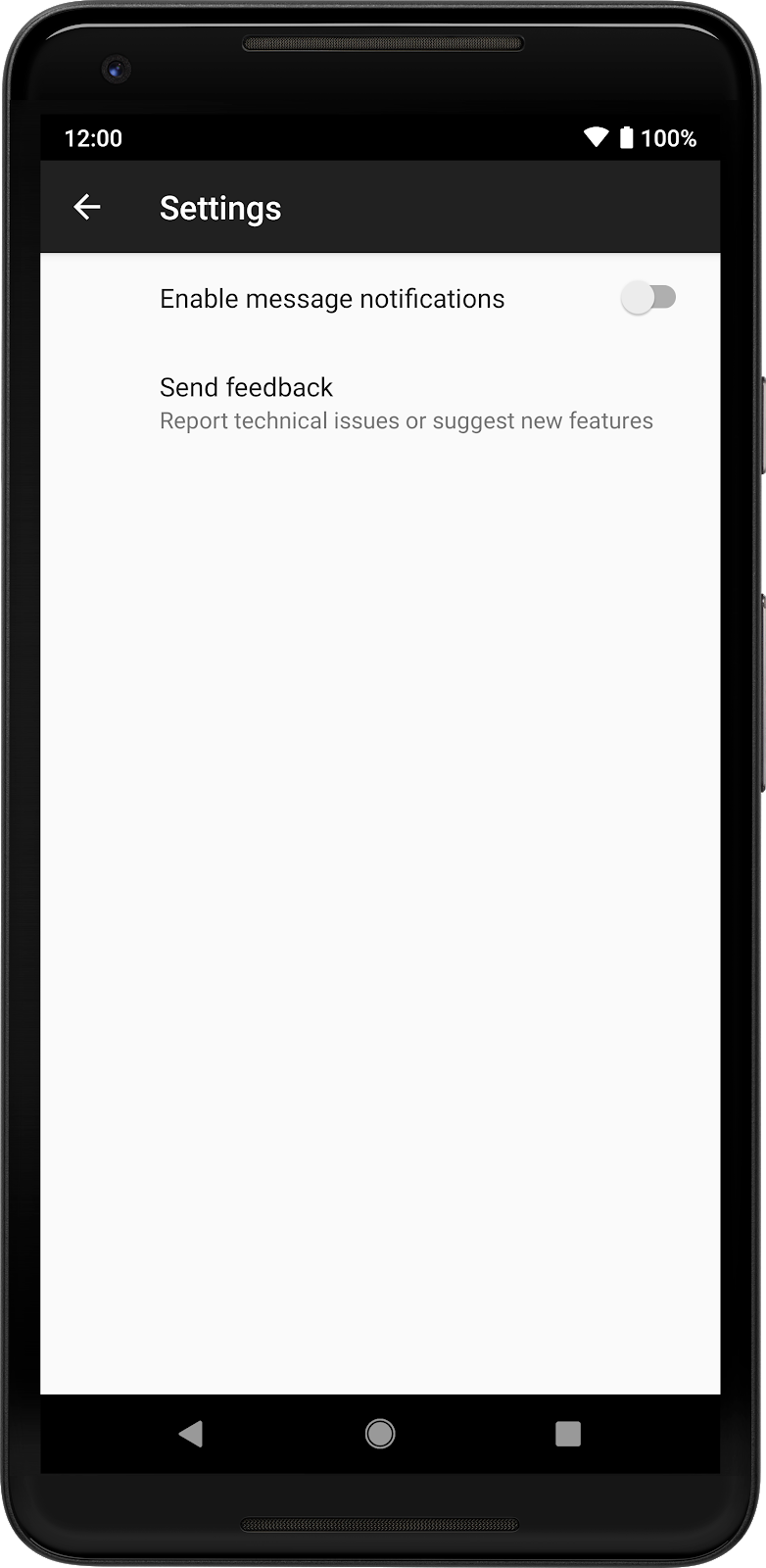
(a). Via XML
<PreferenceScreen
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<SwitchPreferenceCompat
app:key="notifications"
app:title="Enable message notifications"/>
<Preference
app:key="feedback"
app:title="Send feedback"
app:summary="Report technical issues or suggest new features"/>
</PreferenceScreen>
The above xml will give you the following:
(b). Via Code
You can also build a settings screen programmatically via code. Below are code examples:
override fun onCreatePreferences(savedInstanceState: Bundle?, rootKey: String?) {
val context = preferenceManager.context
val screen = preferenceManager.createPreferenceScreen(context)
val notificationPreference = SwitchPreferenceCompat(context)
notificationPreference.key = "notifications"
notificationPreference.title = "Enable message notifications"
val feedbackPreference = Preference(context)
feedbackPreference.key = "feedback"
feedbackPreference.title = "Send feedback"
feedbackPreference.summary = "Report technical issues or suggest new features"
screen.addPreference(notificationPreference)
screen.addPreference(feedbackPreference)
preferenceScreen = screen
}
Adding a [PreferenceCategory is similar, as shown below. Remember to add the children to the PreferenceCategory and not to the root PreferenceScreen:
override fun onCreatePreferences(savedInstanceState: Bundle?, rootKey: String?) {
val context = preferenceManager.context
val screen = preferenceManager.createPreferenceScreen(context)
val notificationPreference = SwitchPreferenceCompat(context)
notificationPreference.key = "notifications"
notificationPreference.title = "Enable message notifications"
val notificationCategory = PreferenceCategory(context)
notificationCategory.key = "notifications_category"
notificationCategory.title = "Notifications"
screen.addPreference(notificationCategory)
notificationCategory.addPreference(notificationPreference)
val feedbackPreference = Preference(context)
feedbackPreference.key = "feedback"
feedbackPreference.title = "Send feedback"
feedbackPreference.summary = "Report technical issues or suggest new features"
val helpCategory = PreferenceCategory(context)
helpCategory.key = "help"
helpCategory.title = "Help"
screen.addPreference(helpCategory)
helpCategory.addPreference(feedbackPreference)
preferenceScreen = screen
}
Conclusion
AndroidX Preference library provides a simple and efficient way to store and retrieve application settings or preferences. By using this library, developers can create a user interface that allows users to easily modify the settings of an application. With its easy-to-use API and support for different types of preferences, AndroidX Preference library is a valuable addition to any Android developer's toolkit.